In 3D art, texture refers to image-based data mapped onto the surface of a 3D model to define its visual properties—such as colors, patterns, and surface details. It defines the visual appearance of a model—such as color, reflectivity, roughness, and pattern—by using 2D image maps like diffuse (color), normal, specular, and displacement maps. Textures play a key role in achieving realism, allowing a plain 3D mesh to appear as wood, metal, fabric, stone, or any other material. By controlling how light interacts with the surface, textures enhance visual detail without adding more geometry, making them essential in gaming, animation, AR/VR, and digital product visualization.
Texture in 3D Art & Scanning
In 3D modeling and scanning, texture refers to the surface details and color information applied to a 3D model, playing a crucial role in making digital objects look realistic by simulating how light interacts with different materials. Without textures, 3D models appear simple and artificial, lacking the intricate details of real-world surfaces. To enhance realism, texture maps are used, which are 2D images applied to a 3D model to simulate material properties.
Common Types of Texture Maps:
Diffuse Map – Defines the base color and patterns of an object without lighting or shading effects.

Normal Map – Manipulates light reflections to create the illusion of small surface details like bumps, grooves, and scratches.
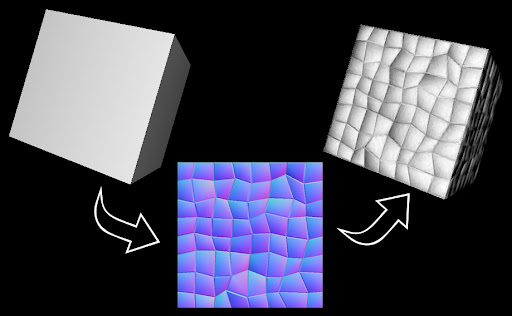
Bump Map – Uses grayscale height variations to simulate depth perception.

Displacement Map – Physically alters the model's geometry to create realistic surface variations.

Specular & Roughness Maps – Control how reflective or matte a surface appears, affecting its material properties.

In 3D scanning, capturing texture is as important as capturing shape, ensuring that digital objects closely resemble real-world counterparts. A 3D scan app like KIRI Engine captures both geometry and texture data, reconstructing highly detailed digital models using photogrammetry—a technique that analyzes multiple high-resolution images from different angles to generate accurate textures mapped onto the 3D model. This results in a fully UV-mapped model with realistic surface details, making it highly useful for games, animation, AR/VR, and digital art. 3D scanning automates texture capture, reducing manual work while maintaining photorealistic accuracy, ultimately improving efficiency in 3D asset creation.
How to Make Textured 3D Art & Its Connection to 3D Scanning & 3D Modeling
Textured art focuses on visually rich surfaces, and 3D scanning technology allows artists to digitize real-world textures and apply them to 3D models for both physical and digital art applications. KIRI Engine's 3D Scan plays a key role in this process by capturing high-quality textures from real surfaces, making it easier for artists to integrate authentic textures into their artwork.
KIRI Engine supports exporting PBR (Physically Based Rendering) materials, including essential texture maps such as Displacement Maps, Normal Maps, and Roughness Maps. These maps are crucial for achieving realistic surface appearances in 3D rendering by simulating depth, lighting, and surface imperfections. With KIRI Engine, users can generate and export these texture layers alongside their 3D models, making them ready for seamless integration into professional workflows in software like Blender, Unity, or Unreal Engine.
How to Make Textured 3D Art Using 3D Scanning & 3D Models
Capture Real-World Textures with a 3D Scan App
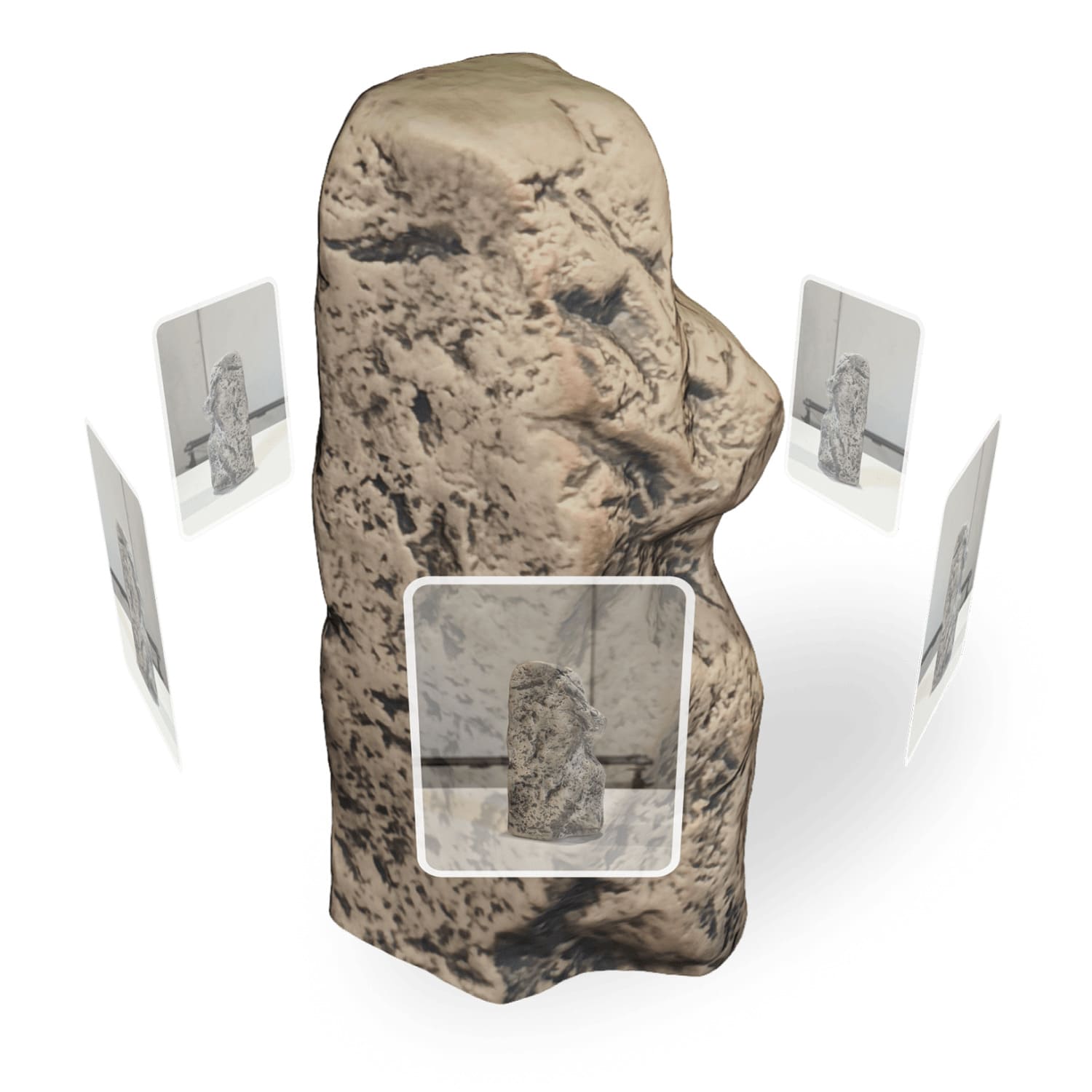

The app captures both geometry and textures, creating a high-resolution 3D model.
Extract and Enhance the Texture
Export texture maps (diffuse, normal, bump, or displacement) along with the created model.
Use Substance Painter, Photoshop, or Blender to refine the texture.
Adjust contrast, sharpness, and colors for a more striking effect.
Apply Textures to 3D Models
Use the extracted textures as materials in 3D modeling software like Blender, ZBrush, Maya, or Unreal Engine.
Apply the textures to walls, sculptures, or digital art projects for realism and depth.
Create Physical or Digital Art
For physical artworks: Use 3D-printed textures for murals, sculptures, or installations.
For digital artworks: Apply textures in games, AR/VR projects, or NFTs.
How KIRI Engine's 3D Scan Helps in Texture Art Creation
KIRI Engine is a powerful 3D scanning app that enhances the creation of textured art in several ways. It provides high-quality texture capture, allowing artists to scan real-world materials with exceptional accuracy, preserving even the finest details that would be difficult to replicate manually. The app ensures seamless 3D model integration by generating UV-mapped textures, making it easy to apply them directly to 3D models without complex adjustments.
Its fast and efficient workflow reduces the time-consuming process of manual texturing while maintaining realistic results, making it ideal for both professionals and hobbyists. KIRI Engine's Photo Scan feature is particularly well-suited for texture art, as it uses high-resolution images to reconstruct surfaces with rich detail and accurate color representation. However, artists should be mindful of strong exposure during scanning, as overly bright lighting can cause washed-out textures, loss of fine details, or inaccurate colors. For optimal texture capture, using soft, diffused lighting is recommended to ensure even illumination.
Whether creating physical sculptures, murals, or digital artwork, KIRI Engine helps artists bridge the gap between the real world and digital creativity, providing a powerful solution for capturing and applying authentic textures.