3D Scanning and 3D Printing: Pioneering an Era of Innovative Manufacturing
3D scanning and 3D printing are transforming manufacturing and design, offering unprecedented precision and efficiency. This article explores how these technologies are revolutionizing object replication and enabling innovative manufacturing processes.
Advancements in 3D scanning and 3D printing technologies have revolutionized the world of manufacturing and design. These innovative technologies have transformed the way objects are replicated, allowing for unparalleled precision and efficiency. 3D scanning involves capturing the physical attributes of an object or environment and creating a digital representation in three dimensions. This process has become more accessible and efficient due to advancements in hardware and software. Various scanning methods, such as laser scanning, structured light, and photogrammetry, are used to capture accurate measurements and create detailed 3D models.
The applications of 3D scanning are wide-ranging and impactful. Reverse engineering and prototyping have been greatly enhanced by the ability to capture the precise geometry of existing objects and create digital models. Industries such as automotive, aerospace, and product design benefit from the analysis and reproduction of complex parts with ease and accuracy. Furthermore, 3D scanning plays a vital role in cultural heritage preservation. Priceless artifacts, sculptures, and historical structures can be digitally documented and preserved, ensuring their legacy is protected for future generations. This technology also allows for the replication of these artifacts, providing access to historical items that were once out of reach.

In the medical field, 3D scanning has revolutionized patient care. By capturing an individual's anatomy with precision, medical professionals can create patient-specific models for surgical planning, orthotics, and prosthetics. This customization leads to improved treatment strategies, enhanced surgical outcomes, and a higher standard of patient care.
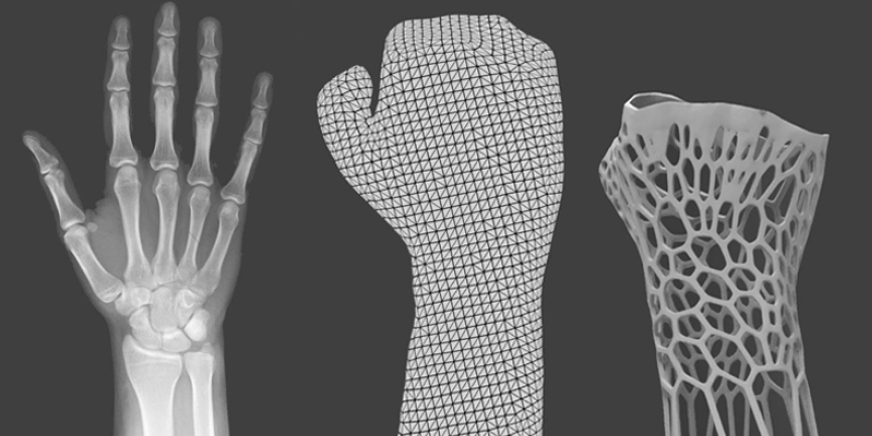
Complementing 3D scanning, 3D printing, also known as additive manufacturing, brings digital designs to life by building physical objects layer by layer. Over the years, 3D printing has seen remarkable advancements, offering a wide range of materials, printing methods, and capabilities. Improved materials, including metals, ceramics, and composites, have expanded the applications of 3D printing, enabling the production of functional end-use parts with greater reliability. The development of large-scale 3D printers has allowed for the creation of larger objects, such as furniture and architectural components. Additionally, modern 3D printers can simultaneously print multiple materials or colors within a single object, allowing for intricate designs and complex geometries with high fidelity.
The integration of 3D scanning and 3D printing technologies has disrupted traditional manufacturing methods. It has brought about cost and time savings by eliminating the need for complex tooling and reducing production time. Rapid prototyping, customization, and on-demand manufacturing have become more accessible and economically viable. Designers and manufacturers now have greater freedom to create complex and innovative designs that were once difficult or impossible to produce. This synergy between scan and print is transforming industries and paving the way for a future of limitless possibilities in manufacturing and design.



